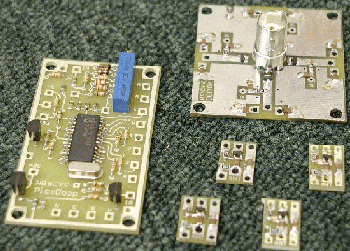
Detailed completion information, to assist final assembly
User Requirements :
The user must finish the assembly of the PicoDopp DF :
User must construct an antenna platform. (see COMPLETION INFO for details )
User must provide and install all the interconnecting cables and connectors.
User must provide and install all the enclosures for the PC boards.
The user must also provide additional equipment to use the PicoDopp DF :
A GPS receiver. ( if GPSS display program will be used )
A VHF FM receiver is required.
A DF display is required : ( one or more of following )
An IBM PC. ( for the GPS and/or IBM display programs )
A PalmOS PDA. ( for the PalmOS display program )
An Economy Pelorus display board ( US$ 30, or make your own )
An Economy Numeric display board ( US$ 50 )
A MultiDisplay board ( pelorus + numeric, US$ 150 )
NOTE 1 : Any combination of these displays can be used simultanously, EXCEPT
the Economy Pelorus and Economy Numeric displays CANNOT be used together.
NOTE 2 : The optional MiniAntenna ( US$ 150 ) can be employed instead of the
standard PicoDopp antenna, if desired. ( simplifies the antenna work )
Specifications :
Rcvr Freq : Determined by user-provided FM receiver, range 100 to 1000 MHz
Antenna : Four elements, ¼ wave vertical with ground plane ( recommended )
Ant Scan : Scan rate 430 Hz, rotation clockwise ( viewed from above antenna )
Ant Switch : Modified Joe Moell Wideband Doppler DF antenna design
Employs Agilent HSMP3893 SMT PIN diodes
SMT / stripline circuit design, BNC output connector
Audio Input : FM receiver speaker audio, 1.0 K ohm load. 25 db dynamic range.
GPS Input : 4800 baud RS232 input, NMEA $GPRMC, $GPGGA and / or $GPVTG messages.
Output 1 : RS232 Agrello DF message, 4800 baud, 8N2. ( 15 messages / second )
Output 2 : IrDA truncated Agrello message, 19200 baud. ( 5 message / second )
Aux Outputs : (1) Eight lines for Economy Pelorus display ( 16 LEDs, scanned, 4 x 4 )
(2) Seven lines for Economy Numeric display ( 4 BCD + 3 strobe )
NOTE : Pelorus and Numeric displays cannot be used simultaneously
Ant Outputs : Four discrete active HIGH outputs for PicoDopp Antenna ( one per antenna )
DC Power : 7 – 14 VDC
Voice Filter : Switched-capacitor filter, ( SCF ) 4 sections. Bandwidth 0.2 Hz
Micro : Microchip PIC 16C773 micro, 1K byte assembly code software
Schematics and Pictorials :
MAIN board [schematic] ( GIF 13 Kb)
ANTENNA / TERMINATION board [schematics] ( GIF 13 Kb)
PicoDopp board [pictorials] ( GIF 20 Kb)
General Description :
The PicoDopp Doppler DF consists of a set of assembled / tested PC boards, intended for amateur or OEM DF applications. It is not a completed instrument, and the user must possess moderate technical skills to assemble the DF into a working unit… The user must also provide an FM receiver, an antenna platform, a display computer, and all the interconnecting cables. Detailed completion information is provided on the [Completion Info] page.
The PicoDopp DF includes 6 PC boards. The MAIN board contains the DF signal detection circuits and data output circuits, to drive a computer and / or local display. The MAIN board is driven by speaker audio from the use-provided FM receiver. The ANTENNA board and 4 small TERMINATION boards are installed at the user-provided antenna platform, and these boards provide switching for 4 antennas that drive the FM receiver RF input.
The PicoDopp is designed for extreme economy and simplicity, but it is actually a very sophisticated DF... It is designed primarily to drive a computer display, consisting of an IBM PC or a PalmOS PDA. Optional "local" display boards are also available, ( see OPTIONS web page ) as well as a more robust ( and complete ) antenna, with an integrated ground plane and antenna / RF output connectors. ( see MiniAntenna ) The PicoDopp is intended for mobile operation, although portable and fixed point operation is also possible.
Minimum System :
The figure below shows the general interconnections for the basic PicoDopp DF system. A more detailed diagram is provided on the [Completion Info] webpage.
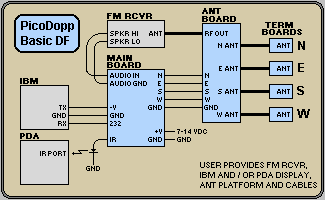
The user can choose to use the IBM PC display and/or the PalmOS PDA display, and/or an optional "local" display board. The Economy Pelorus display and the Economy Numeric display boards cannot be used together, but any other combination of displays can be used, simultaneously.
Additional connections for the optional local displays are provided in the "MORE INFO" website pages for those particular displays : [More Pelorus Info]
[More Numeric Info]
[More MultiDisplay Info]
Description of MAIN board :
The PicoDopp relies heavily on software to achieve extreme economy and simplicity of design. Background information about the general operating principles of Doppler DFs can be found HERE. For those already familiar with basic Doppler DF principles, the following explanation of the PicoDopp MAIN board is provided below.
The PicoDopp uses a switched-capacitor filter ( SCF ) with 4 sections, one for each antenna. The SCF is synchronized with the antenna scan rate, and serves to reject any voice audio that may be superimposed on the FM receiver’s audio output.
The scan rate for the PicoDopp antenna is approximately 430 Hz, and the bandwidth of the SCF is about 0.2 Hz. The SCF sections are selected / de-selected by grounding / un-grounding one end of each capacitor in the SCF. The audio input circuit has diode limiting to protect the microcomputer, but otherwise is completely passive and not ( easily ) vulnerable to audio overload. Input impedance is 1.0K ohm.
The dynamic range of the audio input is about 25 db. Excessive audio input can render the PicoDopp useless, but will not damage it. High audio levels also ( often ) result in severe audio distortion in most FM receiver audio outputs, which can only be confirmed with a scope.
For low level audio signals, the PicoDopp software examines the ( detected ) Doppler signal level to determine if adequate signal is present to generate a bearing with at least 5 degrees of accuracy. If not, the message outputs are suppressed, and the economy display ( if employed, either type ) is blanked. ( NOTE : other external factors may further degrade bearing accuracy… factors which are beyond the control of this design, or any other DF design )
DF bearing calibration is achieved with a ten turn trimpot on the MAIN board. This trimpot allows the user to compensate for any alignment errors between the centerline of the antenna platform, and the centerline of the vehicle. The adjustment range of this trimpot is about 500 degrees, so the antenna can be installed on the vehicle with any orientation desired. The display programs ( IBM PC and PalmOS PDA ) also have provisions for correcting this error ( manual user input ) in software.
The DC voltages that accumulate on the SCF capacitors are proportional to the + and – SINE and COSINE values of the signal direction, observed by the antenna. These values are measured and "differenced" to yield a single value for bearing SINE and bearing COSINE. The SINE and COSINE values are then divided to yield bearing TANGENT, and this result is fed to a simple ARCTAN routine to uniquely identify the bearing angle. The resulting ARCTAN angle value is added to the CALIB trimpot angle value, and corrected ( if required ) for overflow. The final bearing value is then used to generate the various output messages and drive signals for the ( optional ) economy display.
The RS232 output message is transmitted about 10 times per second, and complies with the ( very popular ) Agrello DF message format, as shown below :
Agrello DF message format :
%BBB/Q<cr>
Where % = message start character
BBB = signal bearing degrees ( 000-359 )
Q = signal quality ( 0-9 ) ( fixed @ 7 in this design )
<cr> = carriage return
The RS232 message is transmitted at 4800 baud, with an 8N2 byte format. Negative voltage for the RS232 port is "robbed" from the host computer’s TX line, which is ( otherwise ) ignored.
The IrDA-compliant output IR message is transmitted about 5 times per second, at 19,200 baud. It consists of a truncated "Agrello DF" message. ( %bbb ) Byte format is 8N2. The IR output is current limited and suitable for direct connection to an external IR LED.
Description of ANTENNA Board :
The PicoDopp antenna employs SMT components and a BNC connector for the RF output, to maintain good RF hygiene. Individual antenna connections must be "hard wired" directly to the ANTENNA board, to maintain economy. ( suitable RF connectors were simply too expensive ) Controlled-impedance signal paths ( stripline PCB design methods ) are employed on the board itself, so the ANTENNA board is suitable for use up to 1 GHz and beyond.
The antenna design employs a modified version of the Joe Moell Wideband Doppler Antenna design, which operates by switching each antenna coax line at both ends, using RF PIN diodes. ( in this case, Agilent HSMP3893 SMT devices ) Therefore, four small TERMINATION boards are provide with the PicoDopp, for installation directly at the base of each antenna. ( at the antenna drivepoint ) The DC switching signal for each TERMINATION board is provided through the center conductor of the associated antenna cable.
This "double-ended" switching method yields a wideband antenna design which allows the length of the antenna lines to be arbitrarily selected. ( although all 4 lines must be of equal length, within 1 inch ) Reliable operation of the antenna over multiple octaves of frequency is therefore possible, with the Joe Moell design. This method also substantially reduced RF switching noise that will degrade "weak signal" DF performance.
The GPS Input :
The GPS input is employed to drive the SunningHill GPSS display program, and this input accepts standard 4800 baud NMEA RS232 messages from a GPS receiver. The PicoDopp searches specifically for the NMEA $GPRMC, $GPGGA and / or $GPVTG messages, and ( if found ) re-transmits every 3rd message through the PicoDopp RS232 output, to the display computer. Regular Agrello format DF messages are transmitted at all other times. ( between GPS messages )
If no DF data is available, ( = no DF signal ) the DF messages are suppressed, but the GPS messages will continue to be re-transmitted, when recieved.
If the $GPRMC message is detected, it alone is relayed, ( even if $GPGGA and / or $ GPVTG messages are available ) since the $GPRMC message contains all the information required for the GPSS and WinDopp display programs.
If no $GPRMC message is detected for a period of 8 seconds, the PicoDopp will relay the $GPGGA and / or $GPVTG messages, ( if available ) but will continue to search for $GPRMC messages.
If no GPS reciever is employed, ( or it is turned off, or no data, etc. ) the PicoDopp DF will simply ignore the GPS input, and will not transmit any GPS messages. ( but will continue to search for them )
The main virtue of the GPS input for the PicoDopp DF lies in the fact that it eliminates the need for ( manual ) RS232 switching between the DF output and the GPS output, for the display computer input... Most laptop computers have only one RS232 port, and many newer ones don't even have that... they require a USB-to-serial RS232 "converter" to accept RS232 data. With the PicoDopp GPS input, the data from both sources are "merged together" into a single stream of RS232 data that can be sent directly to the laptop, without the need for any kind of external RS232 switching.... the PicoDopp "fully automates" the switching process.
The user must generally configure the GPS receiver to generate NMEA messages, and sometimes a special cable is required to provide a connection to the GPS.
The SunningHill GPSS Display Program :
The GPSS display program from SunningHill UK is available free to hobbyists and amateur DF users. ( commercial users must negotiate an agreement with SunningHill ) The PicoDopp DF is designed to directly drive the SunningHill GPSS display program, but the program itself is completely separate from the PicoDopp design, and questions about its installation and use must sometimes be answered by SunningHill. ( we will try to answer some questions... )
The GPSS display program is a VERY powerful IBM PC Windows program that generates a "moving map" display of the user's location and DF bearing lines, past and present. When employed, the DF user must simply start everything up and "drive around" for a while, accumulating DF bearings from different locations... the resulting DF data will "accumulate" on the GPSS display screen, and the transmitter location will be revealed by the location where the DF lines intersect... all done automatically.
For more detailed information about the SunningHill GPSS display program, ( and its use with the PicoDopp DF ) please view the More GPSS Info webpage, on this website.
The WinDopp Display Program :
The ( free ) WinDopp display program will run on any Windows IBM PC. It is very similar to the ( very popular ) MsDOS display program, ( described below ) but has several extra features, made possible by the Windows environment. One major feature that is not in the MsDOS program is the ability to use the PicoDopp GPS messages to drive the display compass, yielding an azimuth-stabilized display that fully enables the visual integration features of the program.
The program has a "simulation mode" to allow operation without any DF input, for learning and / or evaluation purposes. Specific details about the program ( and a detailed description of its features ) can be found on the [More WinDopp Info] webpage.
The IBM MsDOS Display Program :
The IBM PC MsDOS display program will run on any IBM computer with RS232 COM ports. ( COM1 or COM2 ) The program is an old-style MsDOS program, to allow use with the widest variety of computers, including very old / inexpensive ones. ( speed may be an issue with very old machines ) The program has a "simulation mode" to allow operation without any DF input, for learning and / or evaluation purposes. Specific details about the program ( and a detailed description of its features ) can be found on the [More IBM Info] webpage.
The PalmOS Display Program :
The PalmOS PDA display program will run on any PDA that uses the ( very popular ) PalmOS operating system, OS version 3.5 or later. It employs the infrared data port ( standard equipment on PDAs ) to provide a fully portable, handheld / cordless Doppler display. The user must provide an infrared LED, driven by the PicoDopp IR output.
The PalmOS display program does not have as many features as the IBM display program, but the convenience of a fully cordless / handheld display, along with the economy of a PDA display ( compared to an expensive laptop IBM PC ) makes this feature quite attractive. NOTE : Some newer models of PDAs may not be capable of IR communications, with this program. Specific details about the PalmOS display program ( its features, and a list of PDAs tested for IR compatibility ) can be found on the [More PalmOS Display Info] webpage.
Optional Display and Antenna Boards :
The basic PicoDopp DF has no "local" display, but such displays are offered as options, should the user desire them. The Economy Pelorus display is a simple, 16-LED pelorus display that connects directly to the AUX outputs on the MAIN board, and provides a simple indicator of the DF bearing, with 22.5 degrees of resolution. ( = 360 / 16 ) The Economy Numeric display consists of 3 numeric readouts to indicate the DF bearing, which also connects directly to the AUX outputs. The user can also build their own versions of these displays, if desired… enough information is provided ( on this website ) to allow that.
NOTE : The Economy Pelorus display and Economy Numeric display cannot be simultaneously employed by the PicoDopp. The required drive signals are different, and the PicoDopp examines a "ground strap" input ( when power is applied ) to determine what type of signals are required on the AUX outputs.
In addition to the economy displays, the MultiDisplay board can be employed to provide a local display of DF bearing. This display has both a numeric and pelorus display, with 36 LEDs for the pelorus, to provide 10 degrees of pelorus resolution. This display also has options to hold / blink the last valid DF bearing, as well as other features. The MultiDisplay board uses the RS232 output of the MAIN board, and it can be tied across this output without causing interference to the primary IBM display, if employed. The MultiDisplay can be simultaneously employed with either the Economy Pelorus or Economy Numeric display, should that configuration be desired.
In addition to the display board options, a more sophisticated and integrated antenna is available, called the MiniAntenna. This is a complete, miniature Doppler antenna, fabricated on a circular PC board of 10 inch diameter. The circular PC board provides a ground plane for the 4 antenna elements ( 5 inches tall ) which mount directly to the MiniAntenna board. The RF sensitivity of the MiniAntenna is not as great as a "full size" ( user provided ) antenna platform, ( especially below 400 MHz ) but the increased convenience of the MiniAntenna can appeal to people who must quickly deploy a DF, especially in situations where weak signal performance is not a critical issue. ( Example : false alarm ELT signals on an airfield ) It is small enough to easily store in a vehicle trunk. ( The user must provide a mounting method for the antenna, and may wish to add a radome enclosure for it )
Further information about these optional boards can be found in the website sections ( under the OPTIONS tab ) that directly describe them :
[More Pelorus Info]
[More Numeric Info]
[More MultiDisplay Info]
[More MiniAntenna Info]
Disclaimers and Caveats :
People without technical skills are discouraged from purchasing the PicoDopp, unless arrangements are made for assistance and support from people with technical skills. People with no prior experience in radio direction finding technology and methods are also admonished not to expect fantastic DF performance from this instrument, simply because it is "hi-tech"… the main factors that limit, degrade, and sometimes defeat DF operation are completely external to the design of this DF, and ( in fact ) external to the design of ANY DF. Examples of DF performance from James Bond movies or episodes of Star Trek are NOT realistic.
More Info and Inquiries :
Additional information about the PicoDopp can be found in the [Completion Info] website section. This section contains more detailed information regarding construction of the antenna platform, IR diode selection for a PDA display, and other issues directly relating to completion work that the user must perform to achieve a working DF. Additional information about the features and operation of the GPSS, WinDopp, IBM and PalmOS display programs can be found in the particular website sections for those programs.
The user is encouraged to review the completion information provided on this website, to get a feeling about the completion work required. If questions or doubts remain, the reader is encouraged to inquire directly by e-mail to the development engineer : [Bob Simmons].